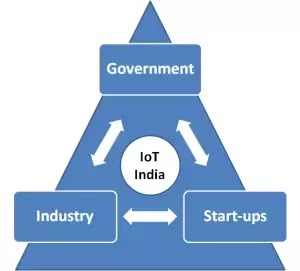
Government:
There is a lot of scope for IoT in India and Government has rightly recognised it and working towards it. The government has taken initiative and framed a draft policy to fulfill a vision of developing a connected, secure and a smart system based on our country’s needs. Government’s objective is to create an IoT industry in India of USD 15 billion by 2020.
One of the key initiatives of the Government is to build smart cities across the country. Major aspects of a smart city being focused by the Government are:
- Smart parking
- Intelligent transport system
- Tele-care
- Woman Safety
- Smart grids
- Smart urban lighting
- Waste management
- Smart city maintenance
- Digital-signage
- Water Management
Other domain specific applications include smart water, smart environment and smart health. There is a plan to incorporate an incubator for to IoT to promote innovation.
Another key initiative taken by Government is the formation of Centre of Excellence on Internet of Things as a joint initiative with NASSCOM. As part of this joint initiative, Government plans to nurture and grow the IoT ecosystem.
With growth comes challenges:
- The biggest implementation challenge will be the complete integration of technology and language. We have to keep in mind India’s diversity.
- Cyber security is another obstacle. We are all well aware that internet and cyber crime are inseparable.
- Issue of last mile connectivity.
Industries:
Another key player in this ecosystem is the Industry. IoT will transform how companies do business when they grab onto its innovations.
Statistics shows about one-fifth of manufacturing companies are using IoT to increase production and reduce costs. Why use IoT? What are the benefits? IoT offers better control of companies’ logistics. The use of the data can also enable them to offer their customers near real-time tracking of shipments. The future of the manufacturing sector in India is envisioned to be capital efficient and flexible. Design updates will be introduced more quickly, and customizations will easily be installed.
Automobile industries are another major adopters aiming to feature-rich, safer and cost effective products and services. They contribute 17% share as adopters. Transforming strategies are being worked upon currently are:
- Usage Based Insurance (UBI) – this enables the device incorporated in vehicles to capture data and transmit it to the IoT platform which is then managed by UBI platform. This will enable insurance companies to build propositions and take it to market.
- Intelligent Emergency Calling (eCall) – It enables cars to automatically call emergency services in case of a serious crash.
- Stolen Vehicle Tracking (SVT) –This is currently implemented
The third largest industry is the IT industry. The world around has evolved with many innovations appearing on a day-to-day basis. These connect machine-to-machine and human-to-machine. Other notable industries that are adopters of IoT are mining, healthcare, banking and education.
Some of the companies who are active in IoT space in India are
- Intel– It is at the top of the ladder in the production of low-power chips to connect IoT devices.
- Volkswagen- It has added an SAP system that keeps track of their parts’ entire supply pipeline to help them track where items are located at all times.
- MediaTek: MediaTek has launched LinkIT ONE development platform which helps design and prototype IoT devices and wearables. They have been working greatly in nurturing and mentoring a lot of start-ups as well.
- Hero MotoCorp- The largest two-wheeler company in the country, with the help of IoT keeps tabs of vehicles available in different locations so that the dealer can be kept informed all the time.
- Hindustan Petroleum- By using IoT, it automates processes and creates real-time insights into the business. It has installed sensors in field units to capture information such as temperature, pressure etc.
- Apollo Hospitals– It has envisioned IoT will transform Health care and are exploring IoT in disease management. SUGAR is their diabetes management initiative which enables constant monitoring of the specific blood sugar levels using IoT enabled technology and transform them to personal health record system. It is also looking at IoT in effective inpatient care, post-discharge care and overall preventive health and wellness.
- Cisco– It is investing in the IoT space by building large teams and localized products.
- Bharti Infratel– It is using IoT for management and live monitoring of its passive infrastructure like tower, fuel management, energy distribution, monitoring and surveillance on the site etc.
- TVS Motor – It uses IoT for process automation, process quality control and traceability in shop floor, pollution control and monitoring, measurement of water flow and power consumption.
- IBM - It is investing heavily in enterprise application infrastructure and databases for connected devices. It is also promoting its cloud-based platform IBM Bluemix heavily amongst the developers.
Start-ups:
Another player in the ecosystem is Startups. Bangalore, Mumbai, Pune and Hyderabad are the four major cities where you would discover quite a few startups that are making a breakthrough. These are silently disrupting and innovating thereby breaking and creating newer realms each day within the IoT space.
One of the pioneering communities in IoT space is IoTBlr which is based out of Bangalore and has been instrumental in driving the IoT ecosystem in India. It is the 2nd largest IoT-focused meet-up community across the world and helps organize different talk, workshops, Hackathons, DIY sessions etc to help spread knowledge and awareness about IoT.
IoT HackDay is another group which is a Pan India initiative based out of Hyderabad. This group conducts Hackathons which helps bring collective knowledge and innovation to address the challenges in IoT and smart cities space. This event works towards addressing social challenges with the use of technology which is the need of the hour.
All in all, India is making progress and we have exciting years to look forward to. The synergistic working of Government, Industry and Startups will drive the eco-system to new heights.
FUTURE OF AI IN INDIA:
Recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI) are a wake-up call to policymakers in India, with every one of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s flagship programs likely to be directly affected within the next few years. With China making rapid progress in AI-based research, it is imperative that India view AI as a critical element of national security strategy. Spurring AI-based innovation and establishing AI-ready infrastructure are thus necessary to prepare India’s jobs and skills markets for an AI-based future and to secure its strategic interests.
The Challenges Facing India’s AI Development
- AI-based applications to date have been driven largely by the private sector and have been focused primarily in consumer goods. The emergent scale and implications of the technology make it imperative for policymakers in government to take notice.
- Early lessons of AI success in the United States, China, South Korea, and elsewhere offer public and private funding models for AI research that India should consider.
- The sequential system of education and work is outdated in today’s economic environment as the nature of jobs shifts rapidly and skills become valuable and obsolete in a matter of years.
For India to maximally benefit from the AI revolution, it must adopt a deliberate policy to drive AI innovation, adaptation, and proliferation in sectors beyond consumer goods and information technology services.
Policymakers should make AI a critical component of the prime minister’s flagship Make in India, Skill India, and Digital India programs by offering incentives for manufacturers, creating regional innovation clusters for manufacturing automation and robotics in partnership with universities and start-ups, incorporating market-based mechanisms for identifying the kind of skills that employers will value in the future, and promoting cloud infrastructure capacity building inside India.
The National Education Policy must make radical recommendations on alternative models of education that would be better suited to an AI-powered economy of the future.
The government should identify public sector applications like detecting tax fraud, preventing subsidy leakage, and targeting beneficiaries, where current advances in AI could make a significant impact.
India must view machine intelligence as a critical element of its national security strategy and evaluate models of defense research in collaboration with the private sector and universities.
Short-Term Actions
In the immediate term, policymakers in India should make AI a critical component of the prime minister’s flagship programs. As an example, within the Make in India program, India must create special incentives for manufacturers, such as relaxing regulations and lowering trade barriers, so they:
- Invest in automation research in India by building research labs and design studios in India
- Create regional innovation clusters, districts, and corridors by building strong linkages around manufacturing automation and robotics between universities and start-ups in India
- Make India a global hub for machine intelligence–based innovation in manufacturing
Similarly, the Skill India initiative should be reworked with the twin objectives of being resilient to skills obsolescence through market-based instruments that tie together the employers, the training institutes, and the students as well as paying special attention to new skills needed to survive in an AI-led economy in the future.
Digital India must be reconfigured to establish cloud infrastructure inside India on a fast-track basis: the limited capacity as it stands today is a critical infrastructure gap and a national security risk. As a part of the Digital India initiative, New Delhi must create specific incentives for building large-scale data centers in India, ideally in partnership with the state governments. The government must identify specific regions in India that are geographically suited for building massive data centers, with an assured supply of power and other critical public infrastructure required for such facilities, and promote these as preferred destinations for investment in cloud infrastructure in India under the Digital India scheme.
The spirit of Startup India, that of creative destruction rather than protectionism, must be allowed to prevail. Recent regulatory decisions in India across cities and states bearing down on taxi aggregators Uber and Ola are regressive and counterproductive; these well-intentioned regulations must be eliminated if AI is to achieve its full potential. Unless the government and domestic industry allow the marketplace to experiment with untested business models enabled by the so-called peer economy, it is unlikely that the economy will create jobs resilient to and in an AI-driven economy. It is imperative to recognize that improving start-ups’ ease of doing business is not merely a regulatory measure to incubate or liquidate a business, but also a free market initiative to allow new and efficient business models to thrive.
For the first time in the history of democratic India, the formulation of a new education policy has been undertaken with a nationwide process of consultation and crowdsourcing. The massive task of analyzing the inputs received and devising the new policy is challenged both by the volume of the inputs and the complexity of myriad issues across India. Formulating the new education policy must not, however, be based solely on inputs received that are affected by current challenges, constraints, and limitations. The National Education Policy must take a long-term view of the skills economy, evaluate the continued relevance of the current system of sequential education, and make radical recommendations on alternative models of education that would be better suited to the economy of the future. Piloting and experimenting in such new models of education must commence in the immediate future before the rapid obsolescence of the current system begins.
Medium-Term Applications of AI in the Public Sector
The government should identify public-sector applications in India where current advances in AI could make a significant impact toward building skills and capabilities domestic applications of AI. For example, New Delhi could:
- Apply AI-based techniques to recognize patterns and learn about tax evasion behavior, in an effort to mine public databases to detect tax fraud and money obtained illegally with the goal of minimizing tax evasion and maximizing tax revenue
- Use AI to scan records, recognize patterns of fraud, and correlate subsidy claims with other consumer data to help detect leakages of subsidies and to learn and better target direct benefits to citizens through interventions most relevant to them
- Develop natural language–processing capabilities to automate multilingual communication and interactivity across a whole range of government services and interfaces, for example, crowdsourcing via MyGov: A Platform for Citizen Engagement towards Good Governance in India, voice calls, automated helplines, and chatbots for the most routine citizen-government interactions
- Use AI-based training and teaching software in various skilling and educational applications
In each of these areas, the government should collaborate with the private sector and university research labs to leverage existing technologies effectively and to rapidly create new technologies to address specific and well-defined problems.
Long-Term Strategy
India must view machine intelligence as a critical element of its national security strategy. At a time when AI is being viewed as a key component of foreign policy between the United States and Japan, with similar proposals of treatment being floated in India, the Indian government must formulate a national strategy on emerging technology trends with long-term strategic consequences.
India must seriously evaluate the DARPA model of defense research in conjunction with private sector and university collaboration in order to create dual-purpose technologies with a scope large enough to allow for development of civilian technology applications. Specifically, the Cyber Grand Challenge model of DARPA needs to be examined for its successful incentivization of academia and the private sector.
India must view machine intelligence as a critical element of its national security strategy.
The proposed National Intelligence Grid (NATGRID) platform, which would link citizen databases, might be a good pilot candidate for creating a machine intelligence–based platform with both national security and civilian benefits and should thus be taken up on a mission mode. Another possibility is Aadhaar, a platforms-based approach to governance founded on massive data sets, which builds on the possibility articulated in Rebooting India.
Authors Nandan Nilekani and Viral Shah enumerate five data-based platforms that could address a broad range of governance challenges. Expanding this list to ten public databases encompassing state and local governments would enable a robust machine intelligence architecture capable of plugging leakages in subsidies, better targeting benefits, and expanding the tax base.
Conclusion
From NATGRID to Aadhaar, machine intelligence–powered platforms can become a strategic instrument of governance in India across a wide range of public services. These platforms are not without their challenges: a machine intelligence–powered approach to governance will require robust digital privacy laws and a code of ethics on limits to using AI. However, the range of AI’s possibilities is so vast that the full spectrum of its opportunities is difficult to fully comprehend. While India may be late to wake up to the AI revolution, Indians of many hues—consumers, technocrats, researchers, and entrepreneurs—are already participants in this revolution with many of Indian origin driving and influencing research in the United States and elsewhere. A clarion call from the prime minister to all of them, to come together and help build an AI ecosystem in India, will go a long way for India to not merely catch up to but to take a quantum leap into the AI-driven future.
Source Links:
IoT League- Internet of things